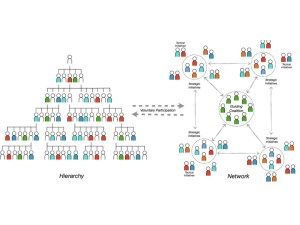
The building of Trusts as Human Organisations offers the best opportunity to exploit the collaborative advantage created by deeply connecting colleagues and groups of schools. Human organisations are deliberately designed to be colleague-centred, relational, collaborative and generative. Aligning individual purpose with the collective mission, empowers colleagues to seek improvement.
Human organisations require deliberate ‘Trust’ leadership to orchestrate collaboration and to understand that Trusts are adaptive, living systems that with the right culture and architecture can trigger greater connection and value. This value is multiplied when peers connect with purpose to explore and exploit their collective imagination and expertise: alchemists creating magic. Too often the capacity and connection for improvement remains latent within Trusts.
“…magic should have a place in our lives – it is never too late to discover your inner alchemist.” Rory Sutherland
The following describes a human organisation—one that seeks a collaborative advantage so that groups of schools perform better than before and are more able to tackle the challenges of our time.
The power of purpose
Human organisations articulate why they exist. Leaders draw maps, set destinations, raise expectations and describe the desired future in technicolour. The narration of the journey and importance placed on it offers the cultural currency, the validation, the reward for collaborating toward the destination.
“Never doubt that a small group of thoughtful, committed citizens can change the world. Indeed, it is the only thing that ever has.” Margaret Mead
A shared quest, in something worthwhile, something meaningful, something that lights a fire, and something anchored in why we exist, creates a generative shared desire and motivation. It sustains and directs energy across the organisation, toward that which is worthy.
Built on relationships3
Human organisations are driven by an unswerving investment in relationships, to secure motivation and to connect peers with purpose, to seek our moral ambition.
“Leadership is communicating to colleagues their worth and potential so clearly that they are inspired to see it in themselves.” Stephen Covey
In human organisations colleagues need to feel the purpose, have enough empowerment and autonomy to seek mastery. It is this investment in colleagues as social beings that taps our deeply engrained tribalist desire, to belong and do meaningful things.
“The relationships we build with each other provide the foundations of change. We are social beings who thrive on connections.” Sir Hamid Patel
The investment in relationships directed toward the purpose is the life blood of human organisations where success is the sum of all decisions made, by all colleagues, every second, of everyday, everywhere in the Trust.
Hard wiring
Human organisations hard wire, design and develop networks and communities as fundamental to their being: seeking connectivity and conductivity. It is not just an exercise in bringing colleagues together, networks must create enough conductivity to shift behaviour and actions intelligently toward the purpose and higher standards.

The architecture and design of networks is very deliberate and requires colleagues to be open, critical and ego-less in the deliberate search for better.
Soft Wiring
“The stars we are given. The constellations we (and they) make.” Rebecca Solnit
Human organisations encourage, permit and expect colleagues to collaborate beyond the set piece networks; connecting in informal, organic and dynamic groups of colleagues motivated to share and solve, in service to the mission. This collaboration propagates value, horizontally and organically across the organisation, adding up to more than the sum of the parts and becoming self-improving.
“…forests are complex adaptive systems, comprised of many species that adjust and learn, …and these parts interact in intricate dynamic networks, with information feedback and self-organisation. System-level properties emerge from this that add up to more than the sum of the parts.” Suzanne Simard
Building a platform
Human organisations invest in platforms of shared approaches for colleagues to collaborate on. This liberates colleagues to add value and seek greater impact by getting much better at the same. Playing in one field, free to innovate and add value based on a foundation, rather than playing in the woods or on the hill or in the fields: where a thousand flowers fail to add value.
This is an intelligent dance, that balances standardised and empowered approaches, and connects colleagues to embed and improve both. For Trusts what should be standardised or empowered is largely objective not subjective, driven by the difference between complicated or complex. The dividend is derived from investing in both.
Empowerment
Standardised approaches liberate rather than stifle schools and enables attention on the quality of education. On this platform, empowerment, sensitive to context generates local ownership and accountability for improvement. Colleagues empowered on the platform to collaborate with colleagues, aligned to the purpose, toward the destination, to drive local improvement is the engine room of self-improvement.
Trusts of parallel ecosystems
Each school is an ecosystem within the wider Trust ecosystem. In their part they run ‘experiments’ in parallel with other schools, with roughly the same resources, on a platform of shared approaches and seeking the same goals (helpful controls). With greater horizontal collaboration between trust leaders and colleagues the conditions exist to compare, contrast, iterate, develop and learn what it takes to add value.
“A golden age is associated with a culture of optimism, which encourages people to explore new knowledge, experiment with new methods and technologies, and exchange the results with others.” Johan Norberg
Seeking improvement requires the transparent sharing of all performance data. A self-improving system requires open access to all performance information to identify the conditions and approaches that secure strong performance.
Alchemy and alloys
Within the ecosystem (a large enough ecosystem) there is the best of everything. With enough connectivity, alchemy, alloying and forging, magic is possible. This is the intelligent melding of contextually sensitive approaches, enhancing a theory of action that is deliberately implemented. This expects heads and colleagues to intelligently exploit the resource in the trust, implementing for impact, and not to blindly stagger from one initiative to another.
“The mythical “butterfly effect” does exist, but we don’t spend enough time butterfly hunting.” Rory Sutherland
Imitation + adaptation
Leaders as alchemists, seek to alloy new approaches and strategies, by iteration, combination and adaptation, to spark greater impact. Deeply connected, open, collaborative cultures can learn from each other and interrogate new ways, ideas and methods to imitate and adapt: utilising the wisdom of the forest in their part of the ecosystem.
“The basic raw materials are a wide variety of ideas and methods to learn from and to combine in new ways.” Johan Norberg
Crowdsourcing
Human organisations create the opportunity and expectation for leaders to crowdsource solutions, tapping into the expertise and approaches of others across the ecosystem: setting out challenges for others to solve. Within a culture of openness, shared responsibility and because we are playing the same game, the ability to crowdsource improvement is the advantage of connected, human organisations.
Self-improving (eco)system
Taken together this forms a blueprint for a human organisation that is purpose driven, relational, generative and seeking value, together. Leaders and colleagues formally and informally networked, often horizontally, engaged in the business of improvement, fuelled by collaborative intelligence and forest wisdom: propagating a high performing ecosystem.
“… beneath the forest floor …exist an ‘underground social network’… trees could move resources around between one another… ‘a co-operative system’, in which trees ‘talk’ to one another, producing a collaborative intelligence … ‘forest wisdom’.” Robert Macfarlane
So, seek greater connectivity to empower and permit colleagues to be alchemists, to collaborate, generate greater value and perhaps create a little magic.
Build human organisations.
Dan Nicholls | August 2025




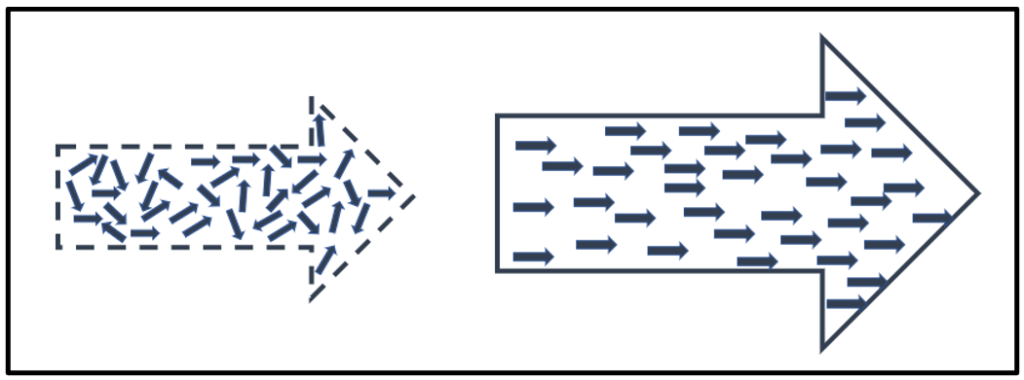









 Overcoming the Resistance of status quo requires a disruptive drive to succeed in achieving non-reversable change.
Overcoming the Resistance of status quo requires a disruptive drive to succeed in achieving non-reversable change.