Strong Trusts seek collaborative advantage by building an organisational structure and curating a culture that connects colleagues in shared endeavour. In these Trusts colleagues are empowered, on standardised platforms, to take collective responsibility for approaches and artefacts that enable connected schools to add value and secure a Trust dividend that sustains beyond their time. Trusts seek school improvement by making deliberate bets, laid as investments, that improve the life chances of all children, particularly those who are under-resourced. And in these dark times, it has never been more important for Trusts to seek greater equity through education, to be long-sighted and to invest in the future by planting trees, deeply rooted in their communities; the shade from which they may never benefit.
“…leaders doing less but understanding more… can free themselves to focus on the future – which is, after all, the proper territory of leadership.” (Tracey Camilleri, et al.)
Where Trusts choose to play and how they focus on the future, matters…
Defined by the decisions we make | Choosing where to play
Whilst we might assume that there are many ways to run a Trust, there are surprisingly few. And it is ‘few’ because all Trusts are in the business of school improvement, held in a highly regulated system and seeking to improve the life chances of all children. There is a reassuring alignment between the challenges and opportunities that Trusts engage with to add value, moderated, a little, by maturity, scale and capacity. Where Trusts choose to play and how well this is enacted largely determines the success of a Trust.
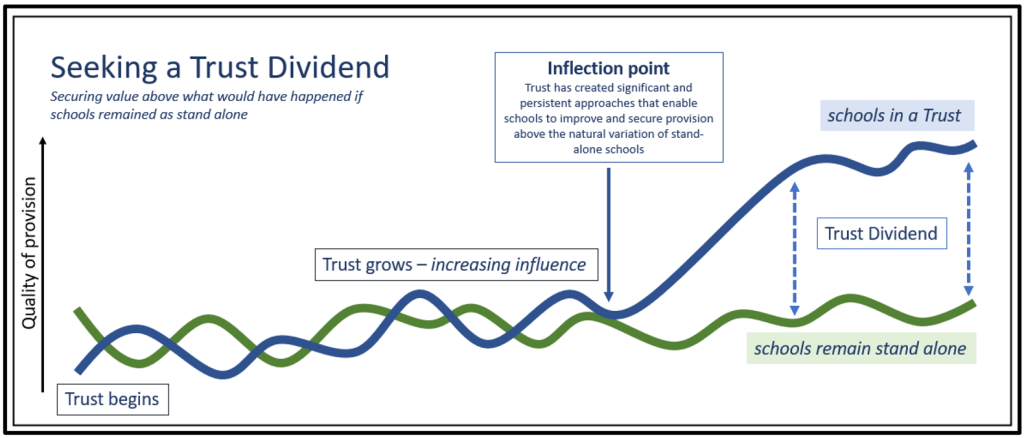
As Trusts grow, merge, mature and forge identities, their effectiveness could be simplified as the sum of all decisions made, by all colleagues, every second, of everyday, everywhere in a Trust that accumulates a dividend, or not. The role of Trust leaders is to influence, nudge, (direct), enable better decisions to be made more often, over time, the sum of which delivers the dividend. How Trusts influence this decision making, is a dance between what it decides to do together and where it decides to empower colleagues to act. An intelligent dance, that balances standardised and empowered approaches, and connects colleagues together seeking a collaborative advantage.
Seeking collaborative advantage | Who’s on first base?
Trust (and school) leaders “…are all playing Moneyball, all the time” (Seth Godin). Seeking the organisational design and strategy that will make a discernible difference and hold schools in a higher and more consistent performance space. For Bill James and the Oakland As it was: “…putting players on base at a higher rate, leads to more runs, which therefore, translates to more wins.” For Trusts, perhaps it is:
“…putting colleagues together (with purpose) at a higher rate, leads to more value, which therefore, translates to a greater dividend.”
Creating the architecture for colleagues to deliberately collaborate creates the conditions for a collaborative advantage. Connecting colleagues within professional networks and subject communities, empowers peers to co-construct and co-design beliefs, attitudes, approaches and artefacts that drive the dividend, for the long term. Strong Trusts understand the need to build antifragile organisations where the hard-wired (and soft wired) collaborative architecture strengthens under stress, secures wide ownership for improvement, is self-improving and irreversible. Effective collaboration is hard to create, what it is and what it isn’t and how it is designed, entirely determines the benefit felt. The biggest influence on teachers is teachers.
“System leaders focus on creating the conditions that can produce change and that can eventually cause change to be self-sustaining.” (Senge et al.)
The cultural landscape and fabric of the Trust
It is hard to under-state the importance of culture in organisations. The deliberate design of the cultural landscape and the strength of the cultural fabric are necessary pre-requisites for the sustained success of any organisation; built ever onward.


Colleagues need a contradictory mix of being part of something bigger (the cultural landscape), and to see themselves in the organisation (part of the cultural fabric), to have what they need and to be a unique part of the pattern.
The cultural landscape of a Trust is shaped and carved over time towards the shared purpose, the mission of the Trust and is guided by deeply held (lived) values and enacted in shared rituals and routines. Walking and working in the cultural landscape reveal the values and character of the Trust; it determines and secures belonging, status, and esteem of colleagues, or not. How Trusts choose to spend time and how colleagues connect is a window into the soul of the organisation.
“The stars we are given. The constellations we make.” (Rebecca Solnit)
The strongest cultural landscapes are organised around the reason for existence. These Trusts clearly articulate the mission and the purpose of the Trust, which is held across the landscape by the North Star, guiding and moulding the norms and behaviours. Lit by this star the cultural fabric weaves colleagues together towards the mission, to do good and make a difference.
“If everything is important, then nothing is… When you know your reason for existence, it should affect the decisions you make.” (Lencioni)
The strongest cultural fabrics are held together by a shared language, vocabulary, norms, behaviours, attitudes, artefacts, standards, conversations, ideas… it holds colleagues, offering the psychological safety to bring their best selves. The fabric is deliberately, consciously and systematically woven in every action and conversation. It is the cultural landscape and fabric of a Trust, that sets the stage and the conditions for colleagues to do important work.
“When we build a culture of people who eagerly seek out and take responsibility, we build a culture that enables a special kind of resilient freedom.” (Seth Godin)
In strong Trusts, culture is deeply linked to where it has been (true to founding) and where it is going (ambition for all) and its journey (the everyday culture). It is (un)surprisingly well designed and felt everywhere, from all colleagues; how we treat anyone, is how we treat everyone. One of those things that takes years to build and seconds to destroy. The culture and colleagues drive the dividend.
Trust Mindedness | school is trust, trust is school. Priming the landscape.
Strong Trusts seed and cultivate the landscape, to reward Trust mindedness, intrinsically so. A priming of culture that is conducive to collaboration, to understanding that all leaders, all colleagues are responsible for all children in the Trust. It is about creating an internal market where the stock price of schools, leaders and colleagues rises with altruism, collaboration, professional generosity, contributing to the shared artefacts, routines and rituals that live out the Trust values, towards the mission and secures the dividend.
This is a Trust-wide mindset, within the cultural landscape and fabric that primes, promotes and rewards relationships and behaviours that fuel and sustain the School Improvement Model. It is the deep collaborative motivation that lives in the Trust, to depth, that encourages better decisions more often, so that the Trust is more than the sum of the parts. Under these conditions Trust leadership is increasingly about guardianship and stewardship.
The primacy of Principals | The lead actors in mature (and immature Trusts)
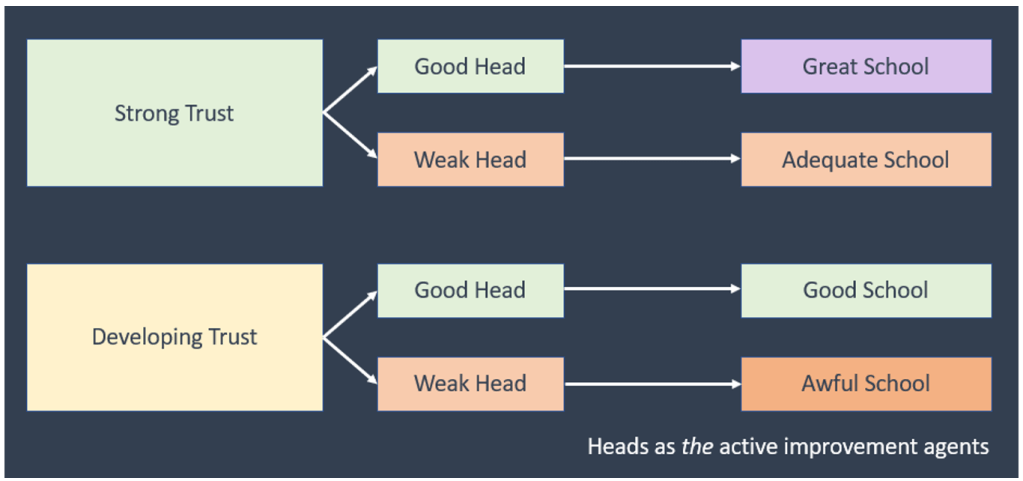
Strong Trusts recognise the primacy of Principals. Schools are significantly influenced by the quality of the headteacher (and teams they lead). If the culture and choices made by a Trust largely determines the potency and effectiveness, then the Headteachers are the key actors in school improvement. The effectiveness of the Headteacher is largely the determining factor in the quality of provision, influenced by the Trust, of course, but perhaps not as much as we would like to think.
The strongest Principals are great with people, understand provision and lead with purpose, prioritising and implementing key strategies and approaches, over time to drive the effectiveness (and efficiency) of the school. Importantly they are open and able to utilise the resource and strength of the Trust; a symbiosis that adds value, and increasingly so. Strong Trusts invest deeply in Headteachers, designing curriculum, professional learning, opportunities, connectivity, collaboration and the conditions for Heads to lead well.
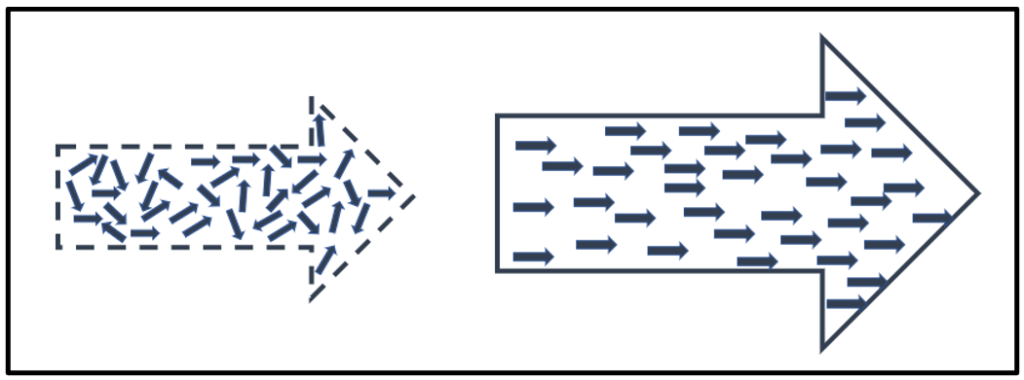
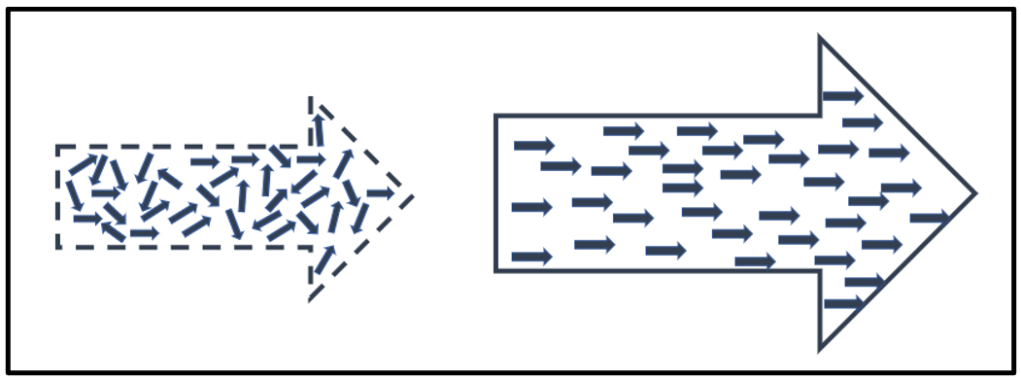
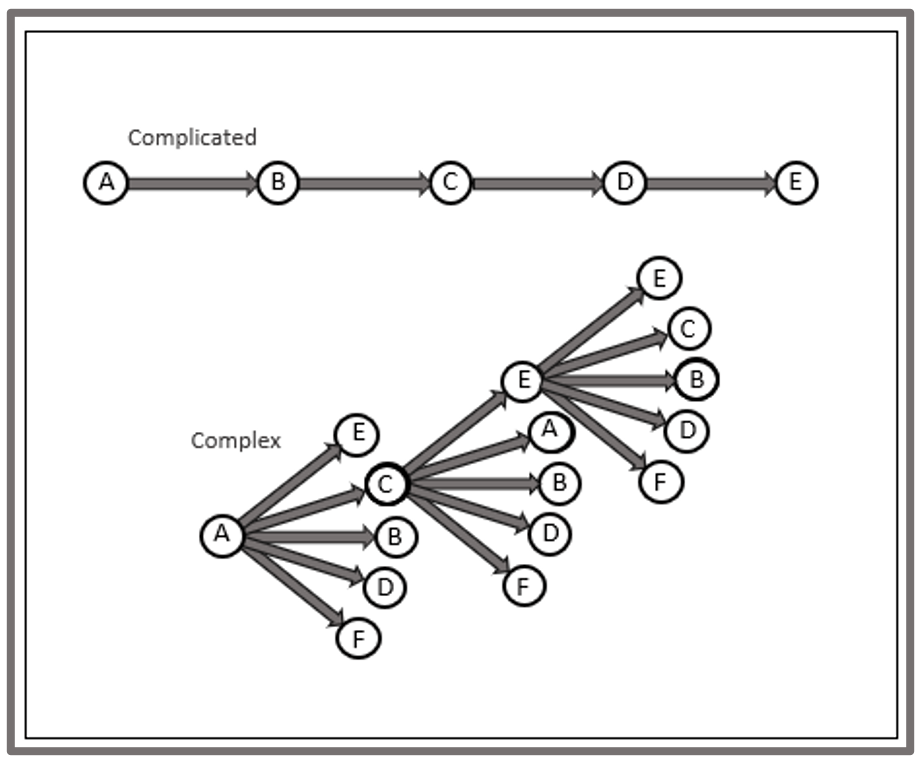
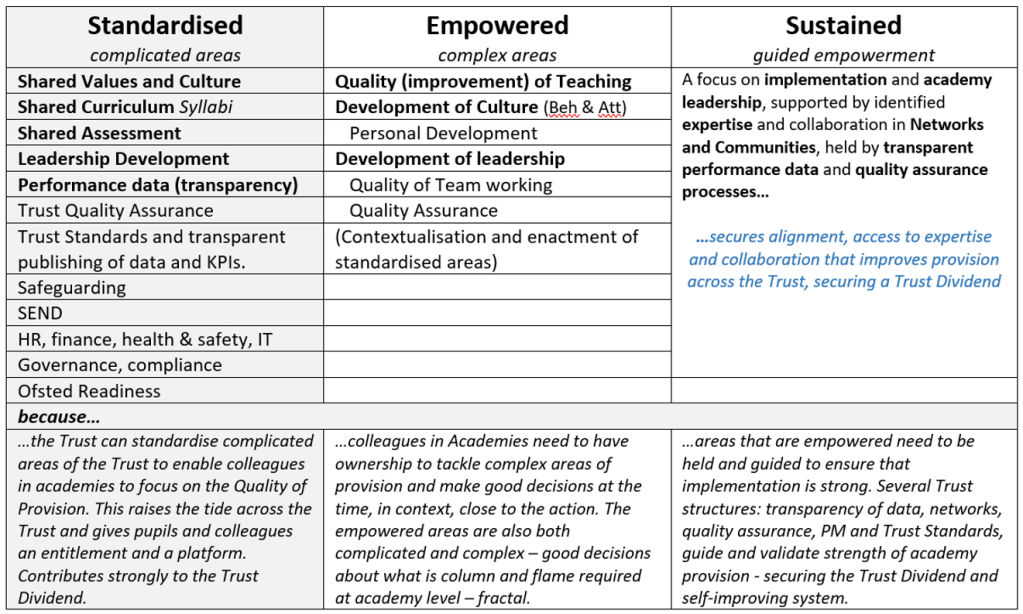
Exploit the complicated | Standardised Provision
Perhaps the biggest advantage afforded to Trusts is the ability to standardise aspects of provision to secure school improvement and greater consistency in provision. Despite some negative connotations or overly simplistic views of “standardisation,” it has tremendous power to liberate, support and give permission (and opportunity) for colleagues to focus on the Main Thing(s). The creation of standardised approaches, strategies and artefacts builds a platform for colleagues, to focus on meeting need, without the distraction of re-designing areas of provision that just need to happen reliably and consistently.
“Leadership is the art of giving people a platform for spreading ideas that work.” (Seth Godin)
Strong Trusts intentionally and deliberately standardise ‘complicated’ areas of provision: Complicated areas act largely the same way each time. These areas can often helpfully be reduced to a checklist; if this, then do that. Trusts should play in these areas and standardise as there is limited need for local decision making or creativity and, importantly, this offers the opportunity for a Trust to improve provision for all learners (and colleagues). Co-creating and co-designing shared curriculum and assessment are particularly potent areas for the dividend.
Empower and guide the complex | Empowered Provision
Areas that are largely complex should be empowered to schools and colleagues. Complex areas respond differently each time and are typically influenced by the unpredictability of human action and interaction, requiring in the moment decision making. In complex areas of provision, we need to push decisions closer to the action where quality and outcomes are linked to the situation as it emerges, contextually influenced.
There are areas of provision in each academy that is better owned and empowered locally, they are largely complex, influenced by context and improved by local decision making. Of course, it is desirable to standardise aspects of these largely complex areas in academies to (fractally) create the standardised platform for colleagues in academies.
Don’t overcook | Just because you could, does not mean you should.
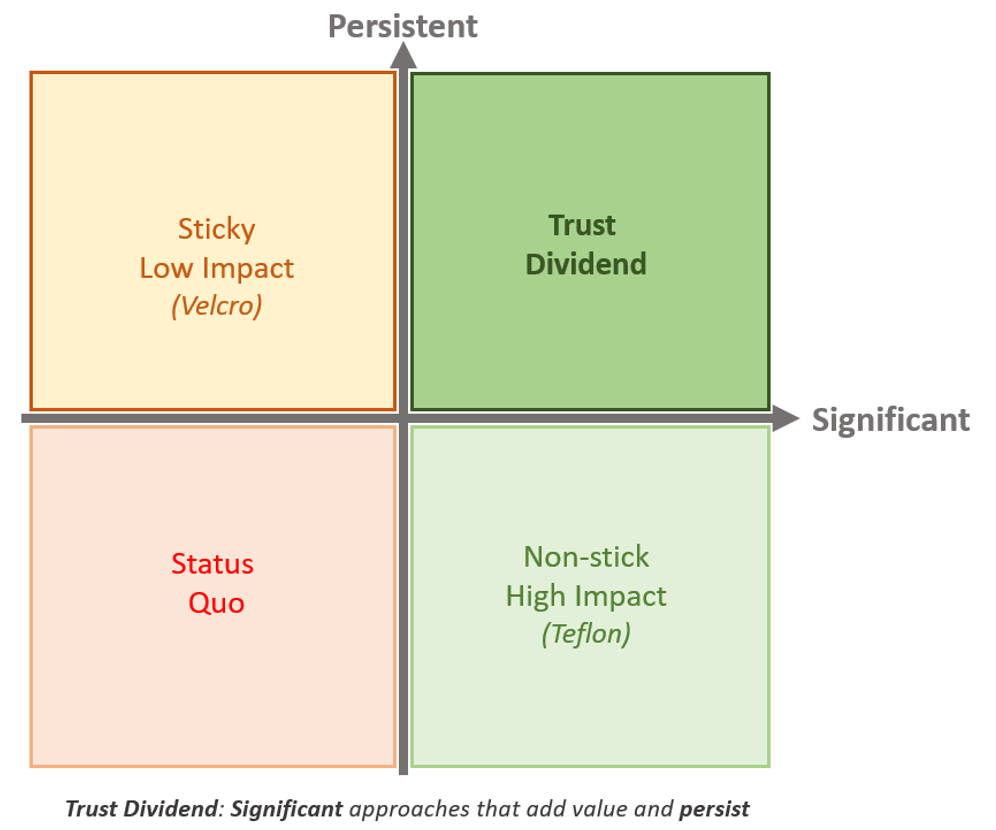
Standardise too far, and you remove the local decision making, professionalism and agency of colleagues to make good decisions, commensurate and appropriate to a profession, and being a professional. This is the crux of effective Trust leadership, the dance between the complicated and complex, to standardise and to empower deliberately and purposefully. Held in tension, strong Trusts create routines, standardise areas of provision to support colleagues, but do not seek to over dictate the complex areas of provision where local decision making, near to the action, informed in the moment, adds the value and creates the sustainable behaviours that secures a self-improving organisation, beyond our time.
Holding ideas in tension is not a compromise
Trusts should not use their power to standardise without bound, there are limits to the effectiveness of standardisation when it steps over and on individual agency and professionalism.
“…under the conditions of true complexity – where unpredictability reigns – efforts to dictate every step from the centre will fail. People … require a seemingly contradictory mix of freedom and expectation.” (Atul Gawande)
Measure what matters, transparently and in the interest of school improvement
Strong Trusts measure what matters and by doing so indicate what they care about. This is the transparent democratisation of data to all colleagues to enable a focus on learning and evaluation of provision, to depth. This reveals standards, informs school improvement and highlights high (and low) performance as well as expertise across the Trust.
Trust leaders are guardians of standards, creating an insurance policy that holds and secures improvement for all children and schools in the Trust. A risk-led approach enables an agile and timely distortion of resource, school improvement capacity and expertise to ensure that all children, areas of provision and academies are supported to improve and level-up in a timescale that is quicker than the local resource capability. School is Trust, Trust is school; all colleagues responsible for all children.
Whether Trusts become more than the sum of their parts and add a dividend for all children, families and communities is determined by the choices that they make and where they choose to play. Strong Trusts craft cultural landscapes and empower colleagues within a cultural fabric, on a standardised platform, to connect across the Trust to realise a collaborative advantage.
“The role of the leader is to enable, facilitate, and cause peers to interact in a focused manner…but still only a minority of systems employ the power of collective capacity.” (Fullan)
Strong Trusts build the conditions where the collective capacity is focused on addressing the steep challenges of our time and where the collaborative advantage drives a dividend that secures greater equity through education.
…But, Trusts are not alone in the landscape, despite pressures that promote isolationism and competition, all parts of the sector are joined in a quest to build a better system. A system that will only meet the growing needs of all children when there is greater collaboration, stewardship, generosity and collective responsibility. We should seek together a sector that exploits a collective collaborative advantage for the good of all children.
All Trusts working together for all children
Dan Nicholls | February 2024
The thinking presented here is based on the work, experience and thinking of colleagues across Cabot Learning Federation.